Filters¶
Filters are used to filter events based on some kind of trigger. For example a structural break filter can be used to filter events where a structural break occurs. In Triple-Barrier labeling, this event is then used to measure the return from the event to some event horizon, say a day.
The core idea is that labeling every trading day is a fools errand, researchers should instead focus on forecasting how markets behave during specific events, movements before, after, and during.
Tip
If you focus on forecasting the direction of the next days move using daily OHLC data, for each and every day, then you have an ultra high likelihood of failure.
You need to put a lot of attention on what features will be informative. Which features contain relevant information to help the model in forecasting the target variable.
We have never seen the use of price data (alone) with technical indicators, work in forecasting the next days direction.
Note
Underlying Literature
- The following sources elaborate extensively on the topic:
Advances in Financial Machine Learning, Chapter 17 by Marcos Lopez de Prado.
CUSUM Filter¶
The CUSUM filter is a quality-control method, designed to detect a shift in the mean value of a measured quantity away from a target value. The filter is set up to identify a sequence of upside or downside divergences from any reset level zero. We sample a bar t if and only if S_t >= threshold, at which point S_t is reset to 0.
One practical aspect that makes CUSUM filters appealing is that multiple events are not triggered by raw_time_series hovering around a threshold level, which is a flaw suffered by popular market signals such as Bollinger Bands. It will require a full run of length threshold for raw_time_series to trigger an event.
Once we have obtained this subset of event-driven bars, we will let the ML algorithm determine whether the occurrence of such events constitutes actionable intelligence. Below is an implementation of the Symmetric CUSUM filter.
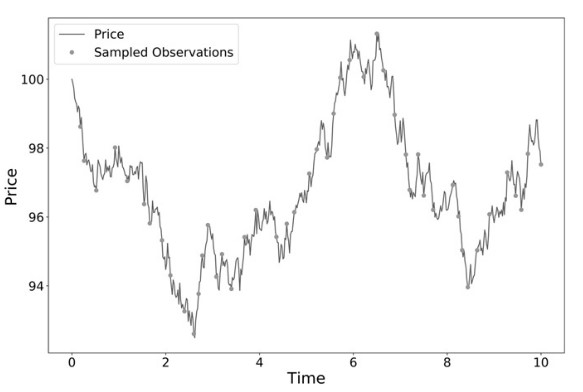
CUSUM sampling of a price series (de Prado, 2018)¶
Implementation¶
Example¶
An example showing how the CUSUM filter can be used to downsample a time series of close prices can be seen below:
Z-Score Filter¶
The Z-Score filter is used to define explosive/peak points in time series.
It uses rolling simple moving average, rolling simple moving standard deviation, and z_score(threshold). When the current time series value exceeds (rolling average + z_score * rolling std) an event is triggered.

