Excess Over Median¶
In this method, a cross-sectional dataset of close prices of many different stocks are used, which is converted to returns. The median return at each time index is calculated and used as a proxy for market return. The median return is then subtracted from each observation’s return to find the numerical excess return over median. If desired, the numerical values can be converted to categorical values according to the sign of the excess return. The labels can then be used in training regression and classification models.
At time \(t\):
If categorical rather than numerical labels are desired:
If desired, the user can specify a resampling period to apply to the price data prior to calculating returns. The user can also lag the returns to make them forward-looking. In the paper by Zhu et al., the authors use monthly forward-looking labels.
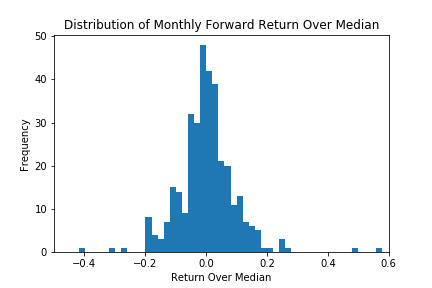
Distribution of monthly forward stock returns. This is the labeling method used in the paper by Zhu et al.¶
Note
Underlying Literature
The following sources elaborate extensively on the topic:
The benefits of tree-based models for stock selection by Zhu, M., Philpotts, F. and Stevenson, M.
Implementation¶
Research Notebook¶
The following research notebooks can be used to better understand labeling excess over median.


